Welcome to BradyBase:
A Database for Soybean Root-Nodulating Bradyrhizobium Species
Bradyrhizobium spp. are slow-growing, Gram-negative, aerobic, non-spore-forming, rod-shaped Alphaproteobacteria bacteria mobile by one polar or subpolar flagellum. Independent studies have described seven species of Bradyrhizobium that nodulate soybean: B. diazoefficiens, B. daqingense, B. elkanii, B. huanghuaihaiense, B. liaoningense, B. ottawaense, B. yuanmingense, and B. diazoefficiens. B. japonicum, B. elkanii, and B. diazoefficiens are used to formulate commercial inoculants around the world and also the commonly reported soybean-nodulating bradyrhizobia in North America.
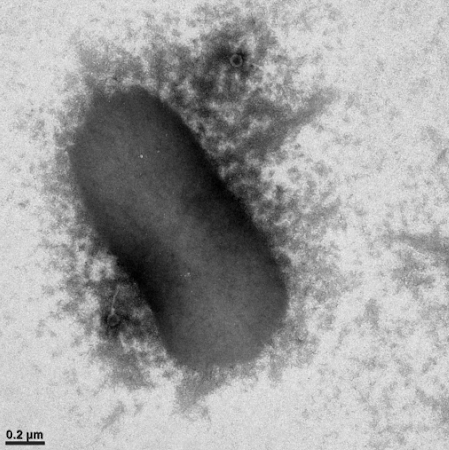
Transmission electron micrograph of a bacterial cell of B. elkanii strain USDA 76 and two lysogenic bacteriophages.
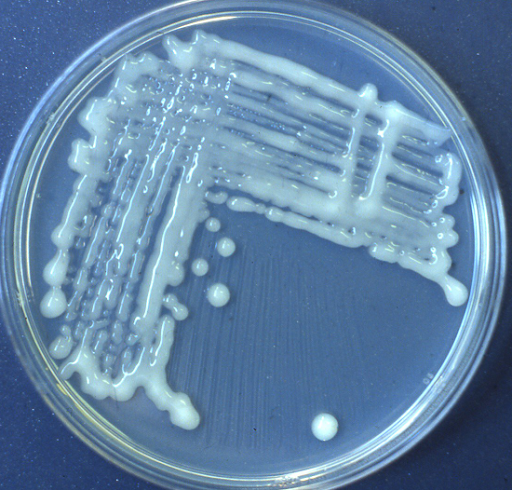
Yeast extract mannitol agar streaked with B. japonicum showing the mucoid colonies typically formed by many representatives of this species.

Soybean plants grown without added nitrogen under greenhouse conditions in response to different inoculation treatments. Control = non-inoculated plants; the remaining pots have plants inoculated with either B. diazoefficiens USDA 110 or B. elkanii USDA 76, the latter displaying rhizobitoxine-induced chlorosis.
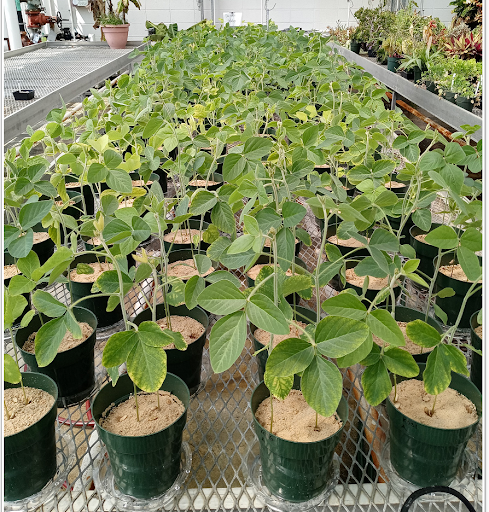

Soybeans grown in the greenhouse without added nitrogen and inoculated with various bradyrhizobia from the University of Delaware Bradyrhizobium Culture Collection (UDBCC).
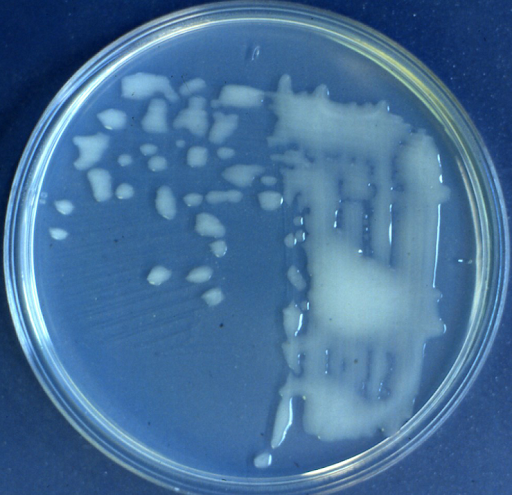
Yeast extract mannitol agar streaked with B. elkanii showing the non-mucoid/watery colonies formed by many representatives of this species.
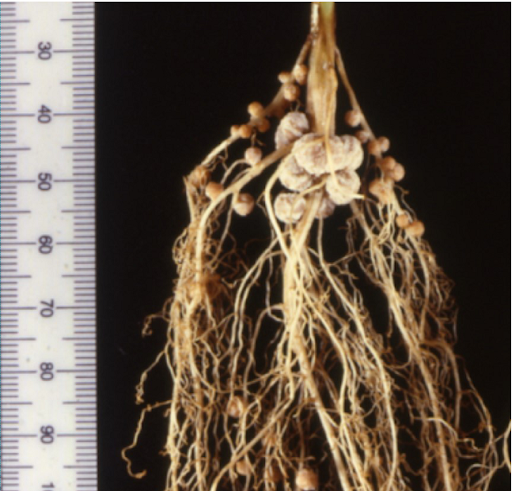
Soybean root system nodulated by Bradyrhizobium.
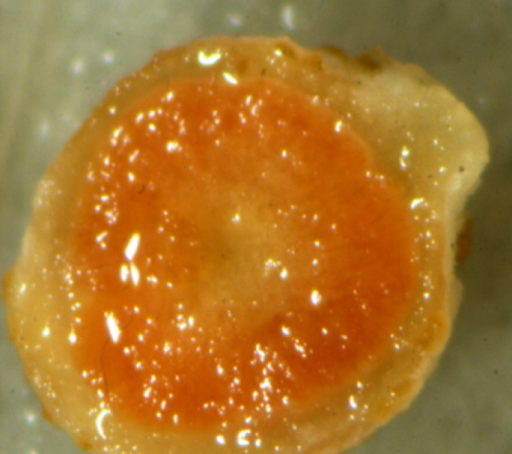
Sectioned soybean root nodule showing red color due to the presence of leghemoglobin.
